So far, the scientific community knows that there are about 280 kinds of worms that can grow and live in the human body and inhabit various organs and tissues. The frequency of human worm infections depends on the climate and socio-economic conditions of a particular territory (in underdeveloped countries, especially those in tropical and subtropical regions, the level of parasitic infection is much higher than in economically developed countries).
The way worms infect humans
- Biological helminth (an animal infection).
- Infectious helminthiasis (spread from person to person).
- Helminthiasis (a disease caused by a parasite that performs one of its life cycles on the earth).
Factors affecting the performance of helminthiasis
- The way the parasite enters the body;
- The degree of adaptation of the worm to the human body;
- Population density (number) of parasitic individuals;
- The habitat of worms (tissue parasites live in the thickness of soft tissue, while intracavitary parasites live in the cavity of hollow organs). Some worms at different stages have both lumen and tissue forms. Usually, the larvae and developmental stages of worms cause more obvious pathological changes.
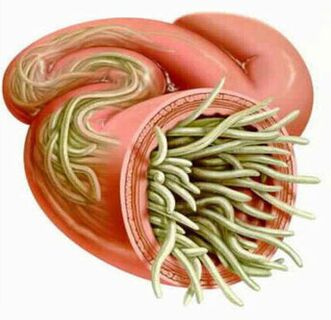
Without re-infection, the number of adult parasites in the human body will not increase. This function can distinguish worm invasion from diseases caused by bacteria, viruses, fungi and protozoa.
Human Worms: Symptoms
Helminthiasis is a disease characterized by two treatment courses (acute, from two weeks to two months) and chronic disease (from months to years).
Symptoms of acute helminthiasis
The initial signs of the disease may appear at different times (the most common is 2-3 weeks, there is worm disease-2-3 days later, there is filariasis, the incubation period can last 6-18 months).
In the acute phase of parasite invasion, the most typical symptom is an allergic reaction (antibodies against antigens of migrating parasite larvae). Usually in people who are infected with worms, a pruritic rash will appear on the skin, which is easy to recur, local lymph nodes increase, systemic or local edema, and muscle and joint pain may occur. In addition, the migration of parasite larvae can also cause chest pain, coughing, choking episodes, stool discomfort, nausea and vomiting.
At the same time, the acute phase of helminthiasis can be accompanied by more serious diseases (severe forms of pneumonia, hepatitis, allergic myocarditis, hepatosplenomegaly (enlarged liver and spleen), meningoencephalitis).The number of eosinophils in the blood increases (increased eosinophils), and the normal quantitative ratio between protein fractions is disturbed (dyslipidemia).
Signs of chronic helminthiasis
The symptoms of the chronic phase directly depend on which organ the parasites "inhabit" in, and their size and number play an important role.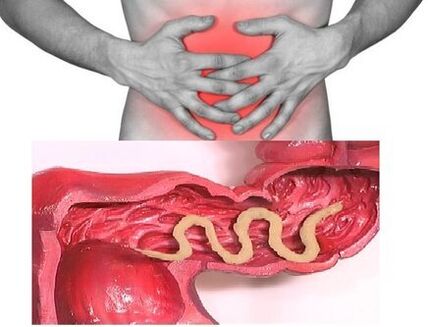 Therefore, when parasitic in the intestine of a single person, the disease may be asymptomatic (the infected parasite is large). The characteristic symptom of the chronic phase of intestinal helminthiasis is indigestion. In children, neurasthenia and pain syndrome are more pronounced. With the massive invasion of roundworms, it may cause intestinal obstruction, obstructive jaundice and pancreatitis.
Therefore, when parasitic in the intestine of a single person, the disease may be asymptomatic (the infected parasite is large). The characteristic symptom of the chronic phase of intestinal helminthiasis is indigestion. In children, neurasthenia and pain syndrome are more pronounced. With the massive invasion of roundworms, it may cause intestinal obstruction, obstructive jaundice and pancreatitis.
In people with helminthiasis, the risk of malignant tumors is significantly increased due to the weakened immune system and the enhanced cell division process (the result of the continuous restoration of tissues destroyed by the parasite).
Types of worms that are parasitic in the human body
There are two types of worms that cause human helminthiasis: round (nematodes) and flat (nematodes and trematodes).
Worms
worm
The parasites that cause small intestinal worms are small, off-white worms that are 10 mm long. The infection occurs in the diet (through the mouth). The reason is dirty hands. The eggs of the parasites can be on the ground of the wool of infected animals, unwashed vegetables and fruits, etc. At the same time, due to intestinal helminthiasis, self-infection cases frequently occur (especially in children), which is caused by the scratching of the worm. The itchy area and subsequent swallowing of eggs.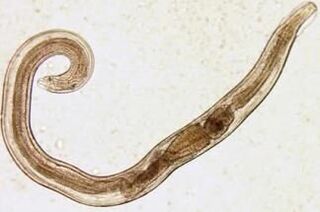 The worm larvae develop in the digestive tract for two weeks. After becoming an adult, the worm parasitizes the small part of the colon and the lower part of the upper part.
The worm larvae develop in the digestive tract for two weeks. After becoming an adult, the worm parasitizes the small part of the colon and the lower part of the upper part.
Even in the larval stage, the worm begins to harm the body of its host, producing enzymes that stimulate the intestinal wall and lead to the development of the inflammatory process. Adult parasites can stick to or penetrate into the deeper layers of the intestinal mucosa, destroying its integrity and assisting in the attachment of secondary bacterial infections. If the pinworm perforates the wall of the small intestine, it may develop peritonitis. Moreover, due to the stimulation of intestinal receptors, the movement and secretion functions of the gastrointestinal tract are destroyed, leading to the formation of gastroduodenitis and enteritis. In childhood, long-term intestinal helminthiasis can cause neurological diseases and delayed physical development.
Scar insect disease
A worm is a red-yellow, large spindle-shaped parasite, reaching 40 cm (female) and 15-25 cm (male) in adulthood. Without suction cups or other fastening devices, the worm can move independently to the food mass. The eggs laid by female parasites are excreted with feces.
When mature eggs are swallowed by water or unwashed vegetables and fruits with soil particles, ass bug infection occurs. After the egg enters the intestine, the larva comes out of the egg. They then penetrate into the intestinal wall, reach the heart through the bloodstream, and then enter the lungs from there. The worm larva passes through the alveoli and enters the oral cavity again through the respiratory tract. After swallowing repeatedly, the parasite reaches the small intestine, where it grows into a large worm. The worm survived for 12 months, then died and was excreted with feces. In the intestines of a host, one person and hundreds of people can survive.
In the intestinal stage of its existence, the roundworm has the ability to move in a spiral and can even penetrate the narrowest opening. This characteristic of the parasite usually leads to the development of quite serious complications (obstructive jaundice or pancreatitis). Allergens secreted by roundworms can cause severe allergic reactions. A large number of adults can cause intestinal obstruction, and worms that enter the respiratory tract can sometimes cause suffocation.
Frasograf
The whipworm eggs laid by the female on the intestinal wall are excreted with feces. Their development takes place in the environment (preferably in the soil). Eggs with parasite larvae enter the body through nutritional means, dirty hands, water or unwashed vegetables and fruits.
There are few helminthiases and no helminthiasis. In the severe stage (with a large amount of infiltration), the patient will experience abdominal pain, severe diarrhea, and sometimes with rectal prolapse. This condition is most commonly observed in frail children. The moderate trichomoniasis stage may cause developmental delays in children.
Trichinella
The causative agent of trichinosis is a small round worm that grows to 2-5 mm. Infection can occur when eating poorly roasted meat (pork, bear meat, wild boar). After the larva of the parasite penetrates the intestine, it will mature in 3-4 days and become a sexually mature individual. The lifespan of the worm is 40 days, after which the parasite dies. By piercing the intestinal wall, the larva enters the bloodstream and is taken to all organs of the human body and sinks into the muscles. In this case, the breathing and facial muscles and the flexors of the limbs are most often affected.
After the larva of the parasite penetrates the intestine, it will mature in 3-4 days and become a sexually mature individual. The lifespan of the worm is 40 days, after which the parasite dies. By piercing the intestinal wall, the larva enters the bloodstream and is taken to all organs of the human body and sinks into the muscles. In this case, the breathing and facial muscles and the flexors of the limbs are most often affected.
In the first few days after the invasion, the patient complained of abdominal pain. Then, about 2 weeks later, the body temperature rose to 39-40 degrees Celsius, an itchy rash appeared on the skin, muscle pain appeared, and facial swelling appeared. During this period, if a large-scale infection occurs, there is a great risk of death. About a month later, the patient recovered. The parasite was wrapped in a spiral and then died within two years.
hookworm and nekator
The biological characteristics of these two parasites and the diseases they cause are similar. In this regard, it is customary to combine them with a common name (hookworm). The length of the worm reaches 10-15 mm and parasitizes in 12 p. intestinal. It should be noted that this is one of the most common parasites, but at the same time, this parasite is rarely found. Worm larvae enter the human body through the skin when they come into contact with contaminated soil. In addition, they enter the bloodstream like round worms, migrate to the lungs, and then enter the digestive tract through the bronchus together with expectorants. The vascular anastomosis is parasitic in the intestine, making itself attached to the intestinal wall. Parasites that feed only on blood bite blood vessels that penetrate the mucous membrane and inject anticoagulant ingredients into them. On average, an adult can absorb 0. 05 to 0. 35 milliliters of blood per day. Therefore, the most typical symptoms of this helminthiasis are iron deficiency anemia and changes in the ratio of protein components (protein abnormalities).
Flatworm
Wide ribbon
This is one of the largest worms with a length of 10-20 meters. The disease caused by this parasite is called dilobite flagellosis. The development cycle of worms begins with freshwater fish or crustaceans. The larvae enter the human body together with eggs or infected fish fillets and are the ultimate owners of tapeworms. After reaching the small intestine, the parasite will attach to the wall of the small intestine and grow into a mature individual within 20-25 days.
Liver fluke
The parasite that causes caterpillar tracheopathy is a flat worm, 7-20 mm long. It should be noted that more than 50% of liver fluke (also known as cat fluke) infections occur in Russian residents. After the eggs enter the fresh water (from the snail that swallowed them), the larvae of the parasite begin to develop. Then they penetrate into the fish (carp, cru fish, sea bream, roach). Eating contaminated fish that has not been sufficiently heat-treated can cause human infections. Liver fluke larvae from the small intestine penetrate the bile duct and gallbladder and are fixed there with two suction cups.
Cow and pork tapeworm
These parasites have almost the same structure, 5-6 meters long. As a result of eating meat from cattle or pork infected by Finns (one of the intermediate forms of helminthiasis), infections with whipworm and whipworm have occurred. Viable Finns appear in the form of whitish bubbles, reaching 0. 5 cm in size, attaching to the wall of the human small intestine, and becoming an adult within 3 months. Banded parasites containing more than 2, 000 fragments are growing. In this case, the end portion containing the egg is broken off and moves independently along the large intestine to the anus, and then crawls out of the anus, or is released into the external environment together with feces. The most typical symptom of helminthiasis is a rupture of the digestive tract.
Echinococcus
For this parasite, one person is the intermediate host. Worms parasitize the human body in the form of Finns. The ultimate owner of Echinococcus ococcus is wolf, dog or cat.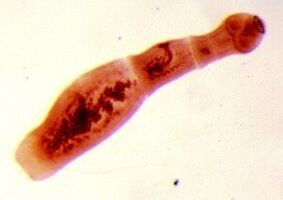 Nutritional infection caused by contact with animals and environmental objects inoculated with Echinococcus eggs. After entering the intestine, cancer balls (six hook larvae) form from their bodies. They enter the bloodstream from the intestines and are transported throughout the body.
Nutritional infection caused by contact with animals and environmental objects inoculated with Echinococcus eggs. After entering the intestine, cancer balls (six hook larvae) form from their bodies. They enter the bloodstream from the intestines and are transported throughout the body.
The "favorite" parasites of worms are the liver and lungs. By colonizing these organs, the larvae become Finn (echinococcal cysts), which gradually increase in size and begin to destroy nearby tissues. Usually, echinococcosis during the diagnosis process is mistaken for benign or malignant tumors. In addition to mechanical shock (squeezing organs and blood vessels), sometimes rupture of the hydatid oc capsule occurs. This condition can cause toxic shock or the formation of multiple new cysts.
Pneumococcus
This parasite is considered to be a kind of echinococcosis and is the cause of one of the most dangerous helminths (pneumococcal disease). Its severity is similar to liver cirrhosis and liver cancer. Infection occurs when the cancer ball (egg with mature larvae) enters the intestine. There, the embryo leaves the egg, penetrates into the intestinal wall, and enters the bloodstream. In addition, with the flow of blood, the parasites will spread to all tissues and organs of the body (in most cases in the liver). There, the main developmental stage begins with the larva (a multi-chambered bubble that forms a duodenal cyst). Each chamber contains the parasite's embryonic head, which continues to develop gradually. Duodenal cyst is a very aggressive structure, which grows continuously due to the increase of bubbles, and has the ability to grow to the liver like cancer metastasis. Necrotic changes caused by vascular dysfunction occur in nearby tissues. Alveolar cocci spread to nearby structures, forming fibrous knots with multiple protruding bubbles. This situation may last for several years and therefore requires mandatory surgical intervention.
Diagnosis of helminthiasis
The diagnosis of worm invasion includes the following activities:
- A detailed history record helps to find out possible causes of infection;
- Stool, blood, intestinal contents 12p, rectal and perianal mucus, muscle tissue, lung sputum, and bile laboratory tests. Analysis may reveal eggs, fragments or fragments of parasites. At the same time, the increase in the content of eosinophils in the blood is also a signal for the presence of helminthiasis.
- When diagnosing diseases caused by larval stages or tissue parasites, serological studies (ELISA, RSK, indirect agglutination, immunofluorescence analysis, etc. ) will be performed.
- Ultrasound, CT and endoscopy are required to detect worms affecting liver tissue.
Worms: Treatment
In the acute phase of parasite infection, patients should receive detoxification and desensitization treatment. In severe cases of disease (liver flukes, trichinosis), glucocorticoids are used according to medical indications.
As a drug for a specific treatment, taking into account the nature of the pathogen, special anthelmintic drugs are required.
At the same time, patients are advised to take antihistamines and intestinal absorbers. The final stage of treatment involves the use of probiotics that normalize the intestinal flora.
also stipulates a special diet (food should be easy to digest and low in fat).
During treatment with anti-worm drugs, patients are required to strictly observe personal hygiene habits (to avoid re-infection). At the same time, for many helminths, all family members and people who maintain regular contact with the infected person must receive treatment.
Prevention of worm disease
- Maintain personal and public health;
- Strictly abide by cooking techniques;
- Regularly check and prevent pets;
- Thoroughly wash fresh vegetables, fruits and herbs;
- Correctly handle river fish;
- Avoid eating raw, slightly salty and dried fish.






































